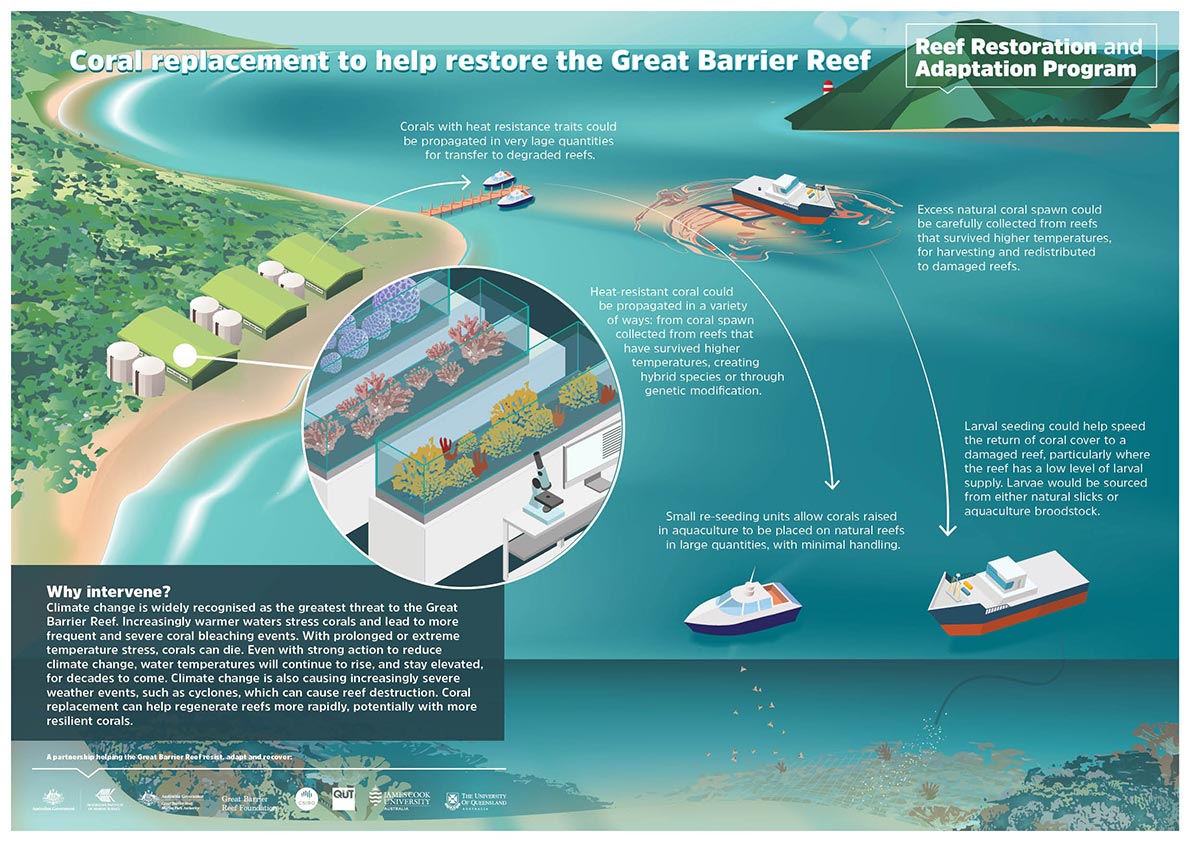
Seeding enhanced corals bred from engineered stock with semi-automated aquaculture
Genetic research at AIMS. Photo: Marie Roman
Functional objective:
Engineered coral performance and reef health
Delivery method:
Seeding enhanced corals bred from engineered stock with semi-automated aquaculture
Deployment scale:
Small (a few hectares, a single reef)
This potential intervention aims to accelerate reef recovery following environmental disturbance by seeding them with genetically engineered or synthetic coral stock and treatments.
Genetic engineering directly manipulates the genetic code of organisms to influence the expression of specific traits. These approaches have been widely used to understand the function of genes, to develop resistant agricultural species and to understand the nature of human disease. Recently-developed gene editing technologies allow researchers to:
- precisely edit genetic material to examine the genetic basis to stress tolerance (such as coral bleaching tolerance)
- potentially change the genetic code to increase stress tolerance or other desirable traits in corals or their microbial partners.
Genetic engineering research greatly facilitates fundamental understanding of corals’ heat tolerance responses, which is required for most, if not all, assisted evolution approaches.
This potential intervention includes methods that target the coral animal and/or its symbiotic microbial partners.
The role of genetic engineering approaches in increasing heat stress tolerance in the coral host, its resident algae and through engineering its microbiome to increase beneficial probiotics, is not yet clear.
Genetically-engineered corals could be propagated either sexually (through coral seeding) or asexually (harvesting coral fragments), using semi-automated, shore-based aquaculture (amalgamating current aquaculture and automation technology with a combination of diver and semiautomated deployment methods from barges and small vessels).
The young corals, attached to a small device or in small fragments, would be deployed from the surface using automated systems on barges and small vessels, to seed reefs.
This approach would require measures to ensure the introduced corals did not harm the local population.
The engineered coral stock may receive additional treatments such as:
- microbial treatments, such as probiotics and manipulating the symbiotic organisms such as microalgae to enhance the performance for future conditions
- hardening (exposure to stressful environmental conditions to induce physiological responses that toughen corals).